Central Asia - Kazakhstan

Kazakhstan, has made significant progress in achieving the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) since adopting the agenda in 2015. Kazakhstan has undertaken a range of measures to promote sustainable development across its economy, society, and environment. Some notable achievements include reducing poverty and inequality, improving access to healthcare and education, and promoting gender equality. In 2022, Kazakhstan presented its second Voluntary National Review (VNR) at the United Nations High-Level Political Forum on Sustainable Development, which highlighted the country’s progress and identified priorities for future action. The VNR also showcased Kazakhstan’s commitment to sustainable development and its efforts to align its policies with the SDGs.
Progress in SDGs
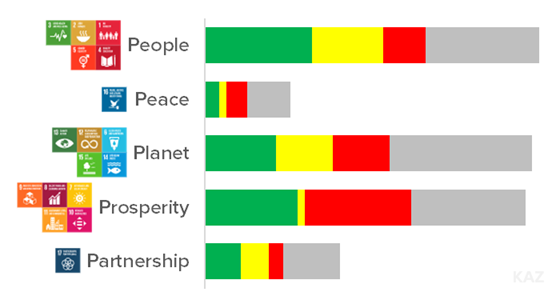
Based on Global SDG Indicators and Diagnostics 🟩 On Track 🟨 Mixed / For Review 🟥 Off Track ⬛ Trends NA
Selected themes
SDG7 in Kazakhstan
SDG7 in Kazakhstan: Ensuring universal access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy for all is an important goal for Kazakhstan. The energy transition is essential for the sustainable future of Kazakhstan’s economy and is one of the SDG Accelerators. Increasing the share of renewable energy and improving energy efficiency are the priorities of Goal 7.
- Problem 7.1. Access to clean energy 🟩 On Track
- Problem 7.2. Renewable Energy 🟥 Off Track
- Problem 7.3. Energy efficiency 🟥 Off Track
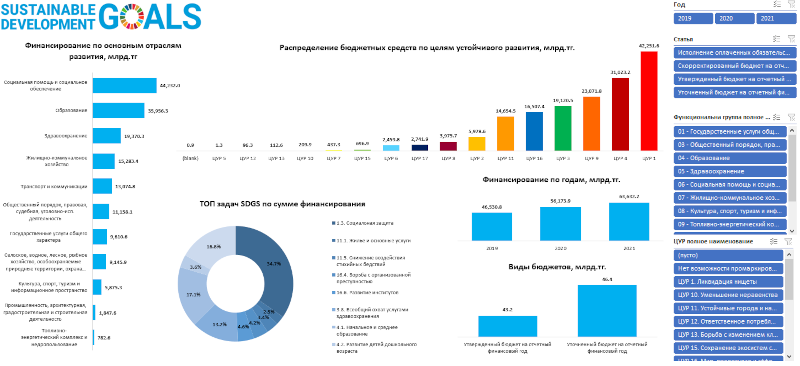
Finances for SDGs
Kazakhsatn conducted Rapid Integrated Assessment includng budget tagging. Besides the National Budget, RIA included budgets for three regions: Almaty city, Karaganda oblast, and the North Kazakhstan Region. RIA was combined with DFA to identify types of flows and provide a comprehensive picture of finances for SDGs.
SDG Accelerators
🔷 2.4: Sustainable food production systems and implement resilient agriculture. Kazakhstan is a net exporter of food products, especially wheat. However, food production systems put serious stress on ecosystems and natural resources (Targets 12.2, 14, 15).
While generally water stress in Kazakhstan is lower than in some neighbouring Central Asia countries, much of the country’s water resources go to agriculture (63%). Climate change will put a serious stress on food production systems through changing water flows. It will require adaptation to new conditions (Targets 13.2, 13.3).
Regional cooperation (Targets 17.10, 17.11) could be a key to increased value added of agricultural products and reduced pressure on natural resources, and to ensure women’s full participation in agricultural practices and climate action (Target 5.5).
🔷 4.4: Skills for employment. In the age of rapid economic and social changes, ensuring relevant skills (Target 4.4) for youth is a crucial accelerator for the whole SDG agenda, as it can accelerate economic growth and make it more resilient. Kazakhstan had a high 15.8 expected years of schooling in 2021. However, the quality of education and equal access remain concerns. In the Program for International Student Assessment (PISA) 2018, students in Kazakhstan scored lower than the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development average in reading (387 vs 487), maths (423 vs 489) and science (397 vs 489). An analysis shows the significant isolation of disadvantaged students from high performing students
Addressing evident differences (Target 10.1) in education (see PISA 2018) the PISA study notes that expanding options for boys and girls will contribute to women’s empowerment (Target 5.5). Sustainable urbanization, including transportation services (Targets 11.1, 11.2), and targeted inclusion policies for disadvantaged groups (Targets 1.3, 10.3) will contribute to improving equality of opportunities
Building future-proof skills improving employability and reducing skills mismatch are essential for achieving sustainable economic growth (Goal 8) and reducing poverty (Goal 1). This will promote equal access to the labour market for women/girls and men and the further empowerment of women to participate into the local labour market (Target 5.5) , including by enhancing their access to Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics and ICT education (Targets 5.5, 5.b).
🔷 7.2. Increase substantially the share of renewable energy in the energy mix. Access to affordable and sustainable energy is crucial for Kazakhstan’s development. The renewable energy share in the total final energy consumption hovered under 2% in the past decade. Coal represents some 50% of the total energy supply, followed by natural gas (some 30%) and oil (close to 20%). Energy prices do not take into account long-term marginal costs and environmental externalities. Energy efficiency (Target 7.3) deteriorated from 8.6 MJ/GDP* in 2010 to 5.38 in 2015 and remained at that level since then. An energy transition is required for the sustainable future of Kazakhstan’s economy
However, an energy transition entails short-term costs. Energy price rises have a negative impact on the most vulnerable segments of the population (Target 10) and must be accompanied by policies to mitigate this impact (Targets 10, 1.3) for Kazakhstan
Renewable and clean energy plays a crucial role in achieving health and gender equality outcomes (Targets 3, esp. 3.9; 5, esp. 5.1., 5.2., 5.4., 5.5, 5.a). Sustainable energy sources contribute to mitigating climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions (Goal 13), promoting renewable energy, and supporting the transition to a low-carbon economy (Goal 12)
Industrialization (Goal 9) will put further demand on ensuring universal access to affordable, reliable and modern energy services, and there will be possible trade-offs between the availability of energy and the use of renewables (Target 7.2).
🔷 10.4: Adopt policies for greater equality. SDG 10.4 calls for the adoption of policies to progressively achieve greater equality in Kazakhstan. The size of Kazakhstan and the variety of its socio-economic and environmntal conditions are driving forces of inequalities, amplified by the varying availability of infrastructure (Goal 9)
Achieving SDG 10.4 has synergetic links with various other SDGs, such as SDG 1 (No Poverty), SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being), and SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth), as reducing inequality contributes to poverty eradication, improves health outcomes and advances sustainable economic development. SDG 10.4 is also intrinsically linked with greater gender equality (Targets 5, esp. 5.1, 5.4, 5.5, 5.b) and women’s empowerment
However, pursuing greater equality may require trade-offs in terms of fiscal adjustments and resource allocations (SDG 17).
The dynamic map shows SDG Accelerators for Kazakhstan.
Use buttons to highlight certain paths and Focus to explore certain targets
See 📊 SDG Push Diagnostic for Kazakhstan
Read the 📑 Integrated SDG Insights Report for Kazakhstan
Voluntary National Reviews
🌐 Voluntary National Review 2022
🌐 Voluntary National Review 2019