SDG Systems
A systems thinking approach is increasingly recognized as essential to achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), given the interlinkages and cross-boundary issues among the 17 goals. We need to unpack these interlinkages and consider the potential synergies and trade-offs among different SDGs. Cross-boundary issues, such as climate change and inequality, can have impacts on multiple SDGs and require coordinated policy responses. This is a crucial element of sustanable development in Central Asia.
To address this complexity, countries are using various SDG complexity tools, such as systems mapping, scenario planning, and social network analysis. For example, Colombia has used systems mapping to identify the interconnections and leverage points among SDGs, while Thailand has used scenario planning to anticipate the potential impacts of external shocks on SDG progress. Other countries such as Ghana, Indonesia, and Mexico have also employed different complexity tools to better understand and address the interrelated challenges of the SDGs.
- Systems mapping - used by Colombia to identify interconnections and leverage points among SDGs: https://www.colombia-sdg.org/
- Scenario planning - used by Thailand to anticipate potential impacts of external shocks on SDG progress: https://siamintelligence.com/en/insights/thailand-2030/
- Social network analysis - used by Ghana to identify key stakeholders and their influence on SDG progress: https://www.ghanaiansdgs.org/
- Integrated planning and reporting - used by Indonesia to align national and subnational plans with SDGs: https://www.id.undp.org/content/indonesia/id/home/sustainable-development-goals.html
- SDG dashboard - used by Mexico to monitor progress on SDGs and highlight data gaps: https://www.gob.mx/sesna/articulos/tablero-nacional-de-indicadores-ods-2030?idiom=es
SDG systems in Central Asia
SDG systems
SDG Push Diagnostics for Interlinkages
Synergies and Tradeoffs
The SDGs do not exist in silos. Understanding the interactions across social, economic and environmental elements of sustainable development is essential to move the needle on the SDGs. SDG Interlinkages show how actions directed towards one SDG can influence the others. Uncovering and understanding these interactions helps in achieving the 2030 Agenda - avoiding the unintended deterioration of the SDGs and their 169 associated targets. The target-level interlinkages are based on the latest available methodology by the KnowSDGs Platform by European Commission. A first literature review (Miola et al., 2019) was updated and expanded in 2021-2022 by a team of researchers who retrieved and analysed all relevant scientific and grey literature* on SDG interlinkages, both in Scopus and Google Scholar.
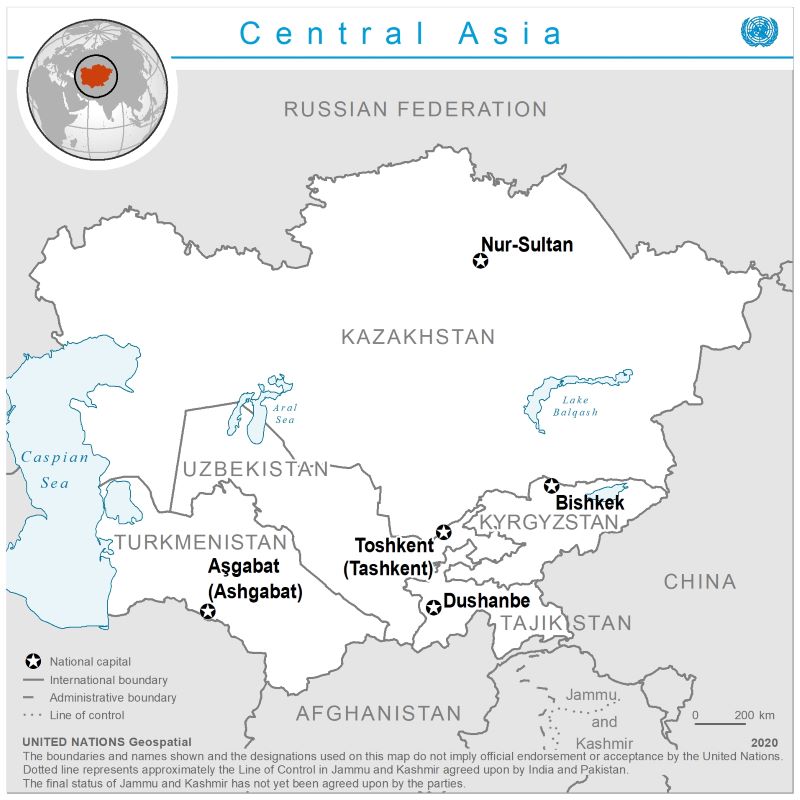
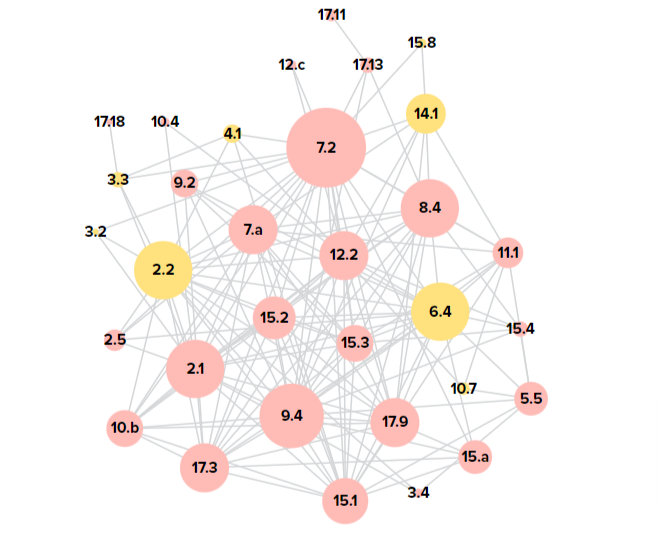
SDG Accelerators for Kazakhstan
🔷 2.4: Sustainable food production systems and implement resilient agriculture. 🔷 4.4: Skills for employment 🔷 7.2. Increase substantially the share of renewable energy in the energy mix 🔷 10.4: Adopt policies for greater equality
The dynamic map shows SDG Accelerators for Kazakhstan
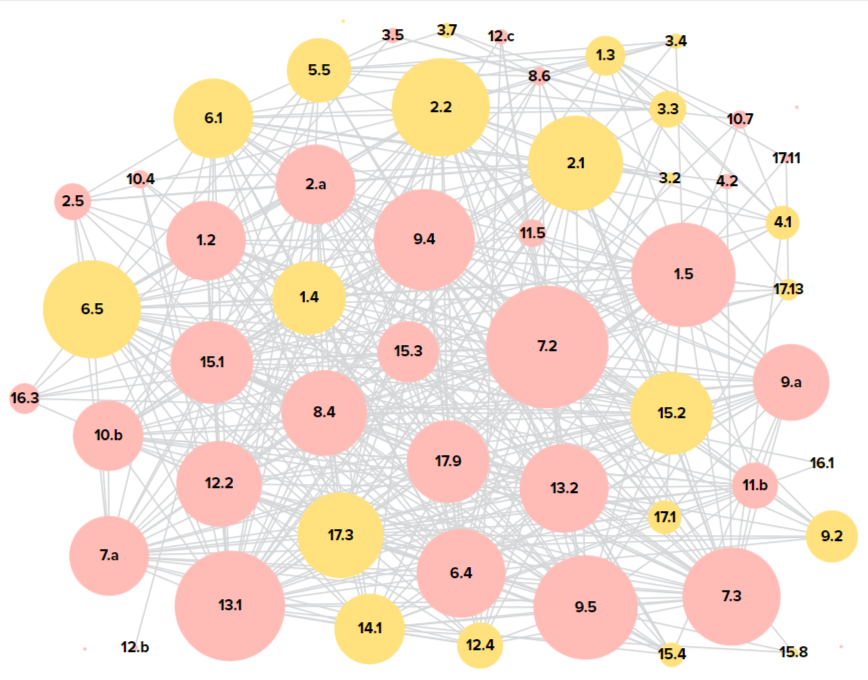
SDG Accelerators for Kyrgyzstan
🔷 2.2. Ensure food security 🔷 4.3. Quality education for everyone 🔷 7.1, 7.2, 7.3. Ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy for all 🔷 8.6. Youth employment and education 🔷 11.1. Safe and affordable housing and basic services
The dynamic map shows SDG Accelerators for Kyrgyzstan
SDG Accelerators for Tajikistan
🔷 2.2. Ensure food security 🔷 4.3. Quality education for everyone 🔷 9.2. Promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization 🔷 11.1. Safe and affordable housing and basic services
The dynamic map shows SDG Accelerators for Tajikistan
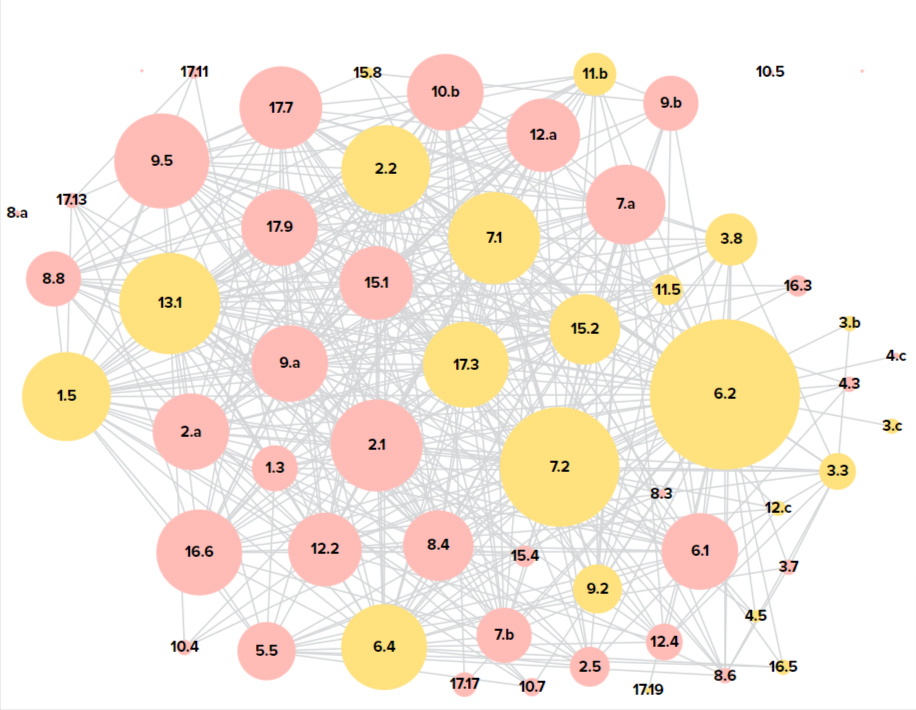
SDG Accelerators for Turkmenistan
🔷 2.3. The agricultural productivity and rural development 🔷 3.4. Reduce mortality from noncommunicable diseases 🔷 4.4. Skills for employment 🔷 6.1. Universal and equitable access to safe drinking water 🔷 8.5. Full and productive employment and decent work
The dynamic map shows SDG Accelerators for Turkmenistan
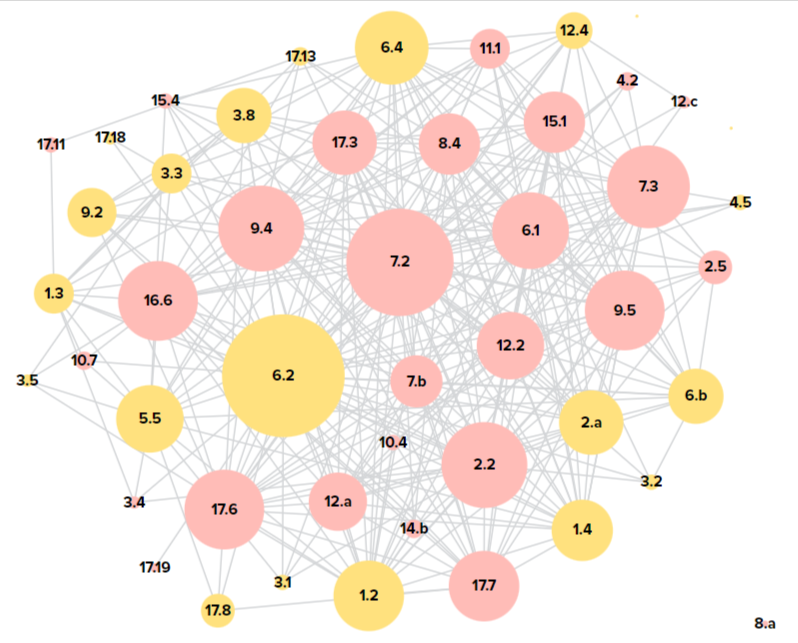
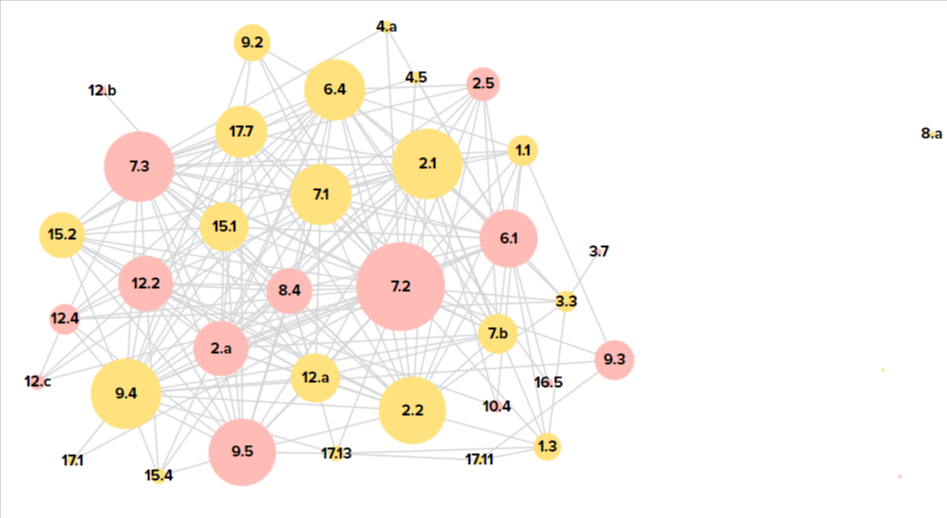
SDG Accelerators for Uzbekistan
🔷 4.3. Quality education for everyone 🔷 8.3. Policies for economic development 🔷 11.1. Safe and affordable housing and basic services 🔷 12.2. The sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources (Green Economy)
The dynamic map shows SDG Accelerators for Uzbekistan
Interlinkages Visualization
 Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan
 Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan
 Tajikistan
Tajikistan
 Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan
 Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan
Cross-border SDG issues
Central Asia, a region encompassing Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan, is a culturally rich and diverse region that has undergone significant social and economic development in recent years. Addressing cross-border issues in Central Asia is the key for achieving SDGs
Water management
Central Asia is home to several major rivers, including the Amu Darya and Syr Darya, which are shared by multiple countries. Disputes over water allocation, infrastructure development, and pollution are common. One solution is to promote regional cooperation through the establishment of joint institutions, such as the International Fund for Saving the Aral Sea (IFAS), which is supported by the EU and UNDP. Other initiatives include the UNDP’s “CAREC Integrated Water Resources Management Project” and the EU’s “Central Asia Water-Energy Nexus Dialogue Platform.”
Energy security
Central Asia is a major producer and exporter of oil, gas, and electricity, but many countries still face energy shortages and rely on imports. There is also a need to promote renewable energy and energy efficiency to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. The EU’s “Central Asia Energy Security Dialogue” and the UNDP’s “Regional Dialogue on Energy Security in Central Asia” aim to promote cooperation on energy policy and investment.
Trade development
Central Asia has enormous potential for trade, but many countries still face barriers to accessing international markets. Promoting trade and economic integration, as well as investing in infrastructure and human capital, can help unlock this potential. The EU’s “Supporting the Implementation of WTO TFA in Central Asia” project and the UNDP’s “Integrated Framework for Trade-Related Assistance to Least Developed Countries” aim to promote trade facilitation and economic growth.
Border management
Central Asia has many porous borders, which pose security risks and can impede trade and travel. Promoting transparency and cooperation among border agencies, as well as investing in infrastructure and technology, can help address these challenges. The EU’s “Border Management Programme for Central Asia” and the UNDP’s “Central Asia Border Security Programme” are working to support these efforts.
Environmental degradation
Central Asia faces many environmental challenges, including desertification, deforestation, and air and water pollution. These issues often transcend national boundaries and require regional cooperation and policy coordination. The EU’s “Central Asia Biodiversity, Ecosystem Services and Climate Change” project and the UNDP’s “Central Asian Desert Initiative” are working to promote sustainable land use and environmental management.